What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a long-term health condition. It happens when your body cannot use sugar (glucose) well. As a result, blood sugar levels become too high. There are two main types of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes means your body does not make insulin. Type 2 diabetes means your body does not use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps sugar enter your cells for energy. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), diabetes affects millions of people worldwide.
Why Is Blood Sugar Control Important?
Keeping your blood sugar in check is very important. High blood sugar can harm your heart, eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Over time, it may also cause serious problems like heart disease or stroke. However, with the right lifestyle changes for diabetes, you can lower your risk of these issues. Good blood sugar control helps you feel better and stay healthy.
Common Symptoms and Risk Factors
Sometimes, diabetes symptoms are easy to miss. Still, knowing them helps you get help early. Common symptoms include:
There are also risk factors for diabetes. These include:
If you notice these symptoms or have risk factors, it is wise to talk to your doctor.
Lifestyle Changes for Diabetes Management
Making healthy changes can help you control blood sugar naturally. Even small steps can make a big difference. Here are some healthy habits for diabetes:
Healthy Eating Habits
First, focus on eating balanced meals. Try to:
For example, fill half your plate with vegetables at each meal. This simple step can help lower blood sugar.
Physical Activity
Next, being active helps your body use sugar for energy. The CDC suggests at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days. You can:
Even short walks after meals can help control blood sugar.
Weight Management
Losing even a small amount of weight can help. For instance, losing 5% to 7% of your body weight may lower your risk of type 2 diabetes. Try to set small, realistic goals. Celebrate your progress along the way.
Stress Reduction
Stress can raise blood sugar levels. So, it is important to find ways to relax. You might try:
Taking time for yourself each day can help keep stress in check.
Sleep Hygiene
Getting enough sleep is key for blood sugar control. Aim for 7 to 9 hours each night. To improve sleep:
Good sleep helps your body manage sugar better.
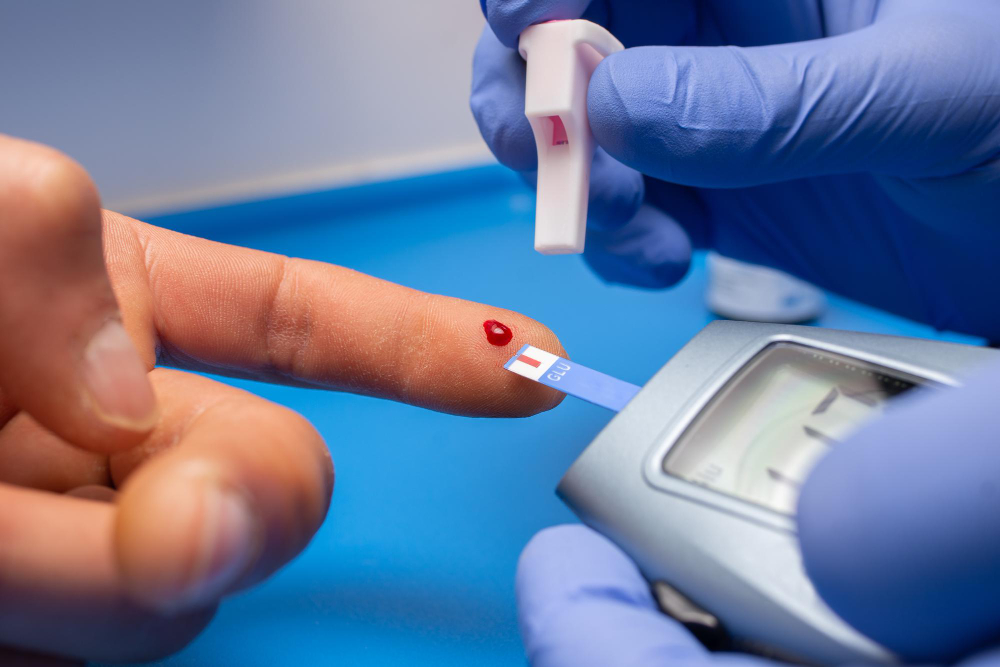
Monitoring Blood Sugar at Home
Checking your blood sugar at home helps you see how your habits affect your health. You can use a simple blood sugar meter. Your doctor will tell you how often to check. Write down your results and share them at your next visit. This helps your doctor adjust your plan if needed.
Practical Diabetes Prevention Tips
Even if you do not have diabetes, you can lower your risk. Try these diabetes prevention tips:
In some regions, local foods may be high in sugar or fat. So, try to choose fresh, whole foods when possible. Ask your doctor about healthy options in your area.
When to Consult a Doctor
If you notice symptoms of diabetes, do not wait. Also, if your blood sugar is often high or low, see your doctor. Early care can prevent problems. Your doctor can help you make a plan that fits your needs.
Conclusion
“To sum up, diabetes is a common but manageable condition. By adopting healthy habits, you can effectively manage your blood sugar levels. Small changes, made consistently, can lead to significant improvements over time. Consult a healthcare professional at Spandan Hospital for personalized advice on managing diabetes and maintaining optimal health.”